picture archiving and communication system (PACS)
What is a picture archiving and communication system (PACS)?
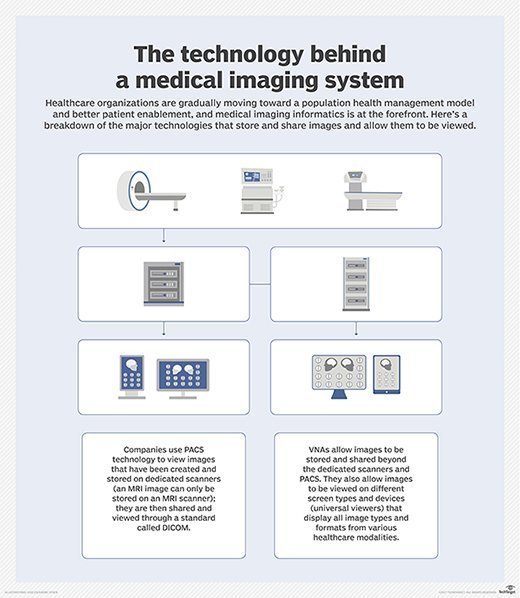
Picture archiving and communication system (PACS) is a medical imaging technology used primarily in healthcare organizations to securely store and digitally transmit electronic images and clinically-relevant reports.
Technologies such as PACS are becoming increasingly important as the volume of digital medical images grows throughout the healthcare industry and sophisticated data analytics of images becomes more prevalent. This is not only because PACS can handle many types of images from many different imaging devices, but also because it enables easy access to the images for diagnostic and medical decision-making purposes.
What is PACS used for?
PACS is used to store, retrieve, present and share images produced by various medical hardware modalities, such as X-ray machines, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans and ultrasound machines. The storage media for PACS can be online (cloud storage) or offline (on-premises).
PACS is predominantly used by radiologists since the area of radiology is traditionally the most prolific producer of X-ray images that need to be stored, retrieved and transmitted. That said, today PACS technologies have also been incorporated into other departments of medicine and healthcare, such as nuclear medicine imaging, cardiology, pathology, oncology and dermatology.
What are the four main components of PACS?
Every PACS has four major components:
- Hardware imaging machines.
- Secure network for the distribution and exchange of patient images.
- Workstation or mobile device for viewing, processing and interpreting images.
- Electronic archive for storing and retrieving images and related documentation and reports.
What are the four main uses of PACS?
In healthcare and medicine, PACS has four main uses:
- May be used instead of hard-copy films and management of physical archives.
- Enables clinicians in different locations to review the same data simultaneously in order to collaborate or consult on a particular case.
- Offers an electronic platform for images interfacing with other health IT automated systems such as a hospital information system (HIS), electronic health record (EHR) and radiology information system to facilitate data-sharing and provide clinicians with a more complete picture of a patient's condition and treatment.
- Allows radiologists and other radiology and medical personnel to streamline and manage the workflow of patient exams.
What are cloud picture archiving and communication systems?
PACS has replaced the need to store and manage hard-copy films and reports. Instead, medical images and non-image data can be securely stored digitally on premises. More frequently, such information is being stored in the cloud.
Cloud-based PACS stores and backs up a healthcare organization's medical imaging data to a secure off-site server. The cloud PACS provider's security is an important consideration since it is mandated by several regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Security Rule in the U.S. This rule and additional HIPAA regulations govern the privacy of patient information. To maintain this privacy, the offsite server must be able to store data securely and incorporate appropriate controls to maintain data security and prevent its compromise by external or internal parties. A cloud PACS also enables medical staff to view medical imaging data from any approved devices, such as smartphones and tablets.
Providers of cloud-based PACS often use a hybrid cloud system in which primary images are stored on the customer's premises and backups are kept in the cloud. Additional types of storage architectures may be configured and attached to the PACS server, such as direct-attached storage (DAS), network-attached storage (NAS) or a storage area network (SAN), each allowing for upgradeability, connectivity, improved protection against failure and added security.
Benefits of picture archiving and communication system
The use of PACS, particularly cloud-based PACS, eliminates the need to manually file and store, retrieve and send sensitive medical information, films and reports. Instead, medical documentation and images can be securely housed in off-site servers and safely accessed from anywhere in the world using PACS software, workstations and mobile devices.
Having ubiquitous digital access to the most updated version of a patient's medical images, clinical reports and history can help clinicians and other healthcare professionals to expedite and improve care, lessening the likelihood of treatment or prescription errors and preventing redundant testing. PACS users can reference the clinical documentation and communicate with each other better to help patients and improve internal processes (billing, testing, discharge, etc.).
Also, since digitization can speed up access to patient information and reduce delays in interpretation, diagnoses and decision-making, it can also improve patient safety. For the same reasons, PACS can save both the healthcare facility and the patient time and money.
Development of picture archiving and communication systems
The modern use of PACS can be attributed to DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine), which is a standard protocol for the management and transmission of medical images and related data. DICOM was originally developed by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and the American College of Radiology (ACR). It enables imaging technologies to connect with and transfer health data to systems at other healthcare organizations.
In 1983, ACR and NEMA formed a joint committee to develop medical imaging technology standards and to facilitate the development and expansion of PACS. Today, nearly all the major medical imaging equipment manufacturers and medical IT companies offer PACS. DICOM provides a standard file format and network protocol to enable the storage and retrieval of medical images in a PACS.
Using PACS with other medical imaging technologies
PACS processes are widely adopted in healthcare. However, PACS vendors employ various syntaxes within DICOM, which can make it difficult to use data from one system in another medical system. Because of the lack of a consistent standard, vendor neutral archive (VNA) technology has replaced PACS in some healthcare settings and integrated with PACS in others.
VNA enables data integration by deconstructing data from an originating PACS and then migrating the data to the new system with the proper syntax.
A radiology information system (RIS) is often used with PACS and VNAs. A RIS is a networked software system for managing medical imagery and associated data. Using it with PACS and VNAs makes it easier to manage image archives, image orders, record-keeping and billing.
Learn about the pros and cons of PACS and VNAs for medical image data storage and see how AI has cemented its role in telemedicine. Explore how generative AI could change healthcare.



