communications security (COMSEC)
What is communications security (COMSEC)?
Communications security (COMSEC) is the prevention of unauthorized access to telecommunications traffic or to any written information that is transmitted or transferred. There are several COMSEC disciplines, including the following:
- Cryptographic security. Encrypts data and renders it unreadable until the data is decrypted.
- Emission security. Prevents the release or capture of electrical or electromagnetic emanations from hardware to defend against unauthorized interception of information or data.
- Physical security. Protects equipment, facilities and other infrastructure from unauthorized access, theft and damage.
- Transmission security. Prevents the interception or disruption of any transmissions occurring over a communications network.
Information technology organizations across all verticals worldwide use these practices to secure their communications. However, the term COMSEC is largely used by the U.S. military and U.S. government.
The U.S. Department of Defense depends extensively on COMSEC practices to safeguard wired, wireless and space communications systems to maintain the nation's defensive posture. Similarly, the U.S. National Security Agency is also a major user of COMSEC cryptographic equipment and technologies as well as a developer of cryptographic algorithms.
Why is COMSEC important?
Most communication today is digital, making it susceptible to unauthorized access by hackers and other malicious actors. COMSEC technologies and practices, such as encryption, reduce the likelihood that sensitive information will be intercepted.
This article is part of
The ultimate guide to cybersecurity planning for businesses
Without COMSEC technologies, any communication could be compromised. Important government, military, business and personal information could be stolen, changed, deleted or otherwise rendered unusable. Data, video, text and voice communication systems could be jammed or disrupted.
If information is stolen by an unauthorized person, such as hackers and cybercriminals, the consequences can range from inconvenient to life-threatening. COMSEC practices are necessary to safeguard the systems that transmit this information and the information systems themselves. Public- and private-sector organizations invest heavily in COMSEC activities to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information.
Who needs COMSEC technology?
COMSEC techniques, technologies and equipment are found throughout all industries and sectors around the world. They protect not only proprietary and sensitive data but also routine communications.
The term COMSEC is usually associated with government, military and national security applications and the classified information those organizations deal with. However, its premise is applicable in the private sector wireless and wired networks as well as both digital and analog communications.
How is COMSEC implemented?
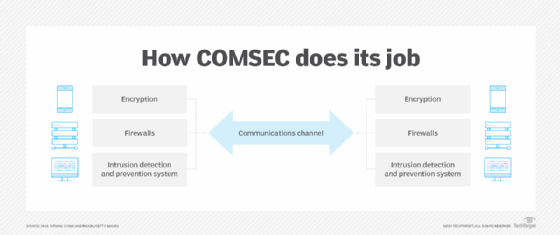
The principal way to protect communications traffic is to encrypt it at the point of origin, when the sender sends it, and decrypt it when delivered to the recipient. So long as the encryption key is secure and known only by the sender and receiver, an encrypted message is likely to remain secure. During transmission and reception of information, additional devices like firewalls and intrusion detection and prevention systems can identify, block and quarantine suspicious communications.
While the premise of a COMSEC program appears simple, in practice, the technologies used to maintain message integrity can be complex. Numerous different encryption algorithms are in use, each of which provides varying levels of protection depending on the requirement. COMSEC equipment and technologies are essential in cybersecurity, as most cyberattacks occur over communications channels.
The importance of cryptography in COMSEC
Encryption is the principal way to protect communications from unauthorized access, disclosure and exploitation. Cryptographic technology converts the original message into a series of indecipherable characters. A digital key is required to encode and decode the data from encrypted to decrypted. So long as the recipient has the correct key, the message can be accessed in its original format.
COMSEC initiatives in government and military organizations continually update and strengthen their cryptographic systems and algorithms to support evolving security requirements.
How is communications security assured?
COMSEC and the resulting information security can be assured so long as several attributes are effectively managed:
- Physical security. The site must be physically secure and prevent unauthorized access to network devices and cryptographic systems. This can include the use of locks, surveillance cameras, security guards, alarms and other security systems and barriers to prevent intruders.
- Communications protocols. Use of secure messaging protocols, especially for internet-based communications and other untrusted networks, can protect communications and provide information assurance. Two common protocol examples are Secure Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security.
- Access protection. Controls like multifactor authentication and role-based authentication limit who can access information and systems.
- Encryption. Cryptography techniques ensure that messages are unintelligible to unauthorized individuals.
- Encryption key management. Encryption keys are used to unlock an encrypted message. A key management infrastructure controls access to keys, restricting their creation, storage, distribution and retrieval to authorized users.
Enterprise communications security is a growing risk. Find out how this is playing out as seen in TechTarget's Enterprise Strategy Group's survey on security threats related to email and other communication tools.






